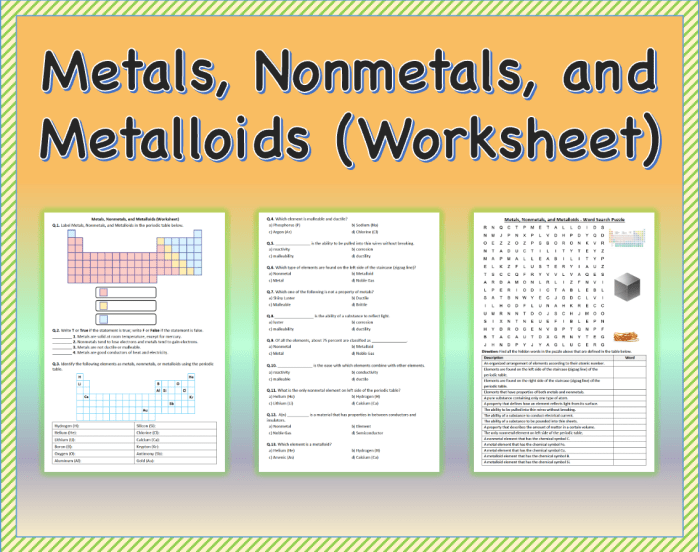
Metals nonmetals or metalloids worksheet – The “Metals, Nonmetals, or Metalloids Worksheet” provides a comprehensive exploration into the captivating world of elements, unraveling their unique properties and diverse applications. This worksheet embarks on an enlightening journey, delving into the fundamental characteristics of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, while shedding light on their indispensable roles in shaping our technological advancements and everyday lives.
As we delve into the intricacies of each element, we will uncover the remarkable physical and chemical properties that distinguish them, gaining a deeper understanding of their behavior and reactivity. Moreover, we will examine the practical applications of these elements, showcasing their significance in industries ranging from electronics to medicine.
Through engaging activities and thought-provoking questions, this worksheet fosters a deeper comprehension of the fundamental principles governing the behavior of matter.
1. Introduction

Metals, nonmetals, and metalloids are three main categories of elements in the periodic table. They are classified based on their chemical and physical properties. Metals are known for their shiny appearance, good electrical and thermal conductivity, and malleability. Nonmetals, on the other hand, are typically dull, poor conductors of electricity and heat, and brittle.
Metalloids, as the name suggests, exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals.
2. Properties of Metals
Physical Properties:, Metals nonmetals or metalloids worksheet
- Shiny appearance
- High density
- Solid at room temperature (except for mercury)
- Malleable (can be hammered into thin sheets)
- Ductile (can be drawn into thin wires)
Chemical Properties:
- React easily with oxygen to form oxides
- Lose electrons easily (electropositive)
- Good conductors of electricity and heat
3. Properties of Nonmetals
Physical Properties:, Metals nonmetals or metalloids worksheet
- Dull appearance
- Low density
- Exist in various states at room temperature (solid, liquid, or gas)
- Brittle (break easily)
Chemical Properties:
- React with metals to form ionic compounds
- Gain electrons easily (electronegative)
- Poor conductors of electricity and heat
4. Properties of Metalloids
Physical Properties:, Metals nonmetals or metalloids worksheet
- Intermediate appearance between metals and nonmetals
- Variable density
- Can exist in various states at room temperature
- Semi-brittle
Chemical Properties:
- Can exhibit both metallic and nonmetallic properties
- Can form covalent or ionic bonds
- Semiconductors (conduct electricity under certain conditions)
5. Applications of Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids
Metals:
- Construction (steel, aluminum)
- Transportation (cars, airplanes)
- Electronics (copper, gold)
- Jewelry (gold, silver)
Nonmetals:
- Plastics (carbon, hydrogen)
- Fertilizers (nitrogen, phosphorus)
- Glass (silicon)
- Medicine (iodine, chlorine)
Metalloids:
- Semiconductors (silicon, germanium)
- Solar cells (silicon)
- Optical fibers (silicon dioxide)
- Light-emitting diodes (gallium arsenide)
Expert Answers: Metals Nonmetals Or Metalloids Worksheet
What is the difference between metals, nonmetals, and metalloids?
Metals are characterized by their shiny appearance, good electrical and thermal conductivity, and malleability. Nonmetals, on the other hand, are typically dull, poor conductors of electricity and heat, and brittle. Metalloids exhibit properties that are intermediate between metals and nonmetals.
What are some examples of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids?
Examples of metals include iron, copper, and aluminum. Examples of nonmetals include oxygen, hydrogen, and chlorine. Examples of metalloids include silicon, germanium, and arsenic.
What are some applications of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids?
Metals are used in a wide range of applications, including construction, transportation, and electronics. Nonmetals are used in a variety of applications, including plastics, fertilizers, and fuels. Metalloids are used in a variety of applications, including semiconductors, solar cells, and glass.