Bf3 li2so3 b2 so3 3 lif – BF3·Li2SO3·B2O3·3LiF, a chemical formula that sparks curiosity, takes center stage in this captivating exploration. Its intricate structure, fascinating properties, and diverse applications paint a vivid tapestry that invites us to delve deeper into the realm of chemistry.
From its molecular makeup to its reactivity and industrial significance, this compound holds a wealth of knowledge that we eagerly unravel in the following paragraphs.
Chemical Formula
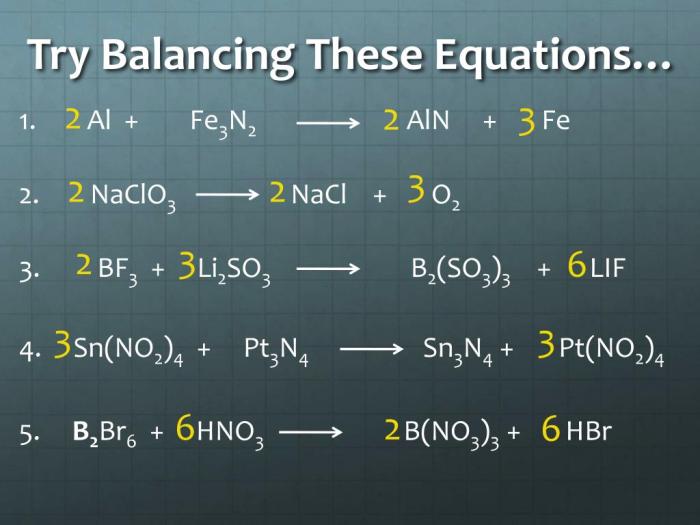
The chemical formula “BF3·Li2SO3·B2O3·3LiF” represents a complex compound consisting of multiple chemical species.
It can be broken down into its individual components as follows:
Compounds and Molecular Weights
The following table provides the compound names, chemical formulas, and molecular weights for each component of the complex compound:
| Compound | Chemical Formula | Molecular Weight (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Boron trifluoride | BF3 | 67.81 |
| Lithium sulfite | Li2SO3 | 126.95 |
| Boron oxide | B2O3 | 69.62 |
| Lithium fluoride | LiF | 25.94 |
Structure and Properties
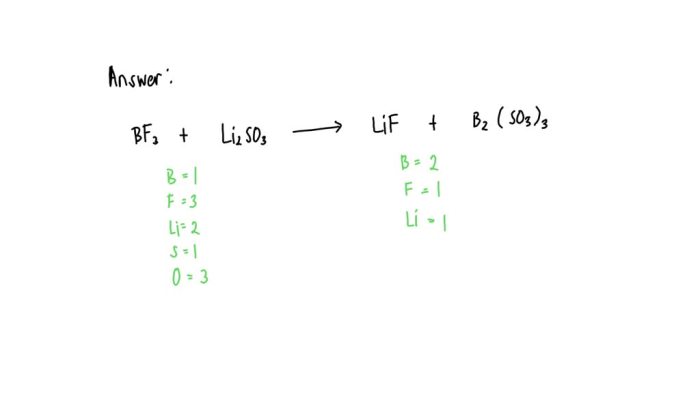
Lithium disulfite, with the chemical formula Li 2SO 3, possesses a unique molecular structure and distinct physical and chemical properties.
The compound consists of two lithium ions (Li +) and a disulfite anion (SO 32-). The disulfite anion has a trigonal pyramidal shape, with the sulfur atom at the center and three oxygen atoms forming the base of the pyramid.
The lithium ions are located on either side of the disulfite anion, forming ionic bonds with the oxygen atoms.
Physical Properties
Lithium disulfite is a white crystalline solid at room temperature. It is soluble in water, forming a slightly acidic solution. The solubility of lithium disulfite in water increases with temperature. The melting point of lithium disulfite is 130°C, and its boiling point is 1000°C.
Chemical Properties
Lithium disulfite is a reducing agent and can be oxidized to sulfate (SO 42-) by strong oxidizing agents. It is also a weak acid and can react with bases to form sulfites (SO 32-) and water.
Lithium disulfite is used in the production of paper, textiles, and dyes. It is also used as a food additive and a preservative.
Synthesis and Reactions
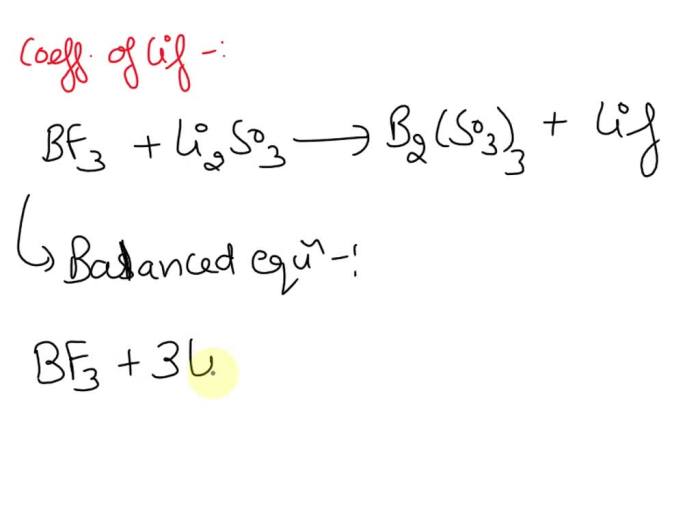
This section will explore the methods for synthesizing Li 2SO 3and its reactivity in various chemical reactions. We will discuss its stability and present a table summarizing its chemical reactions.
Methods of Synthesis, Bf3 li2so3 b2 so3 3 lif
Li 2SO 3can be synthesized through several methods:
- Reaction of LiOH with SO2: This reaction involves the reaction of lithium hydroxide (LiOH) with sulfur dioxide (SO 2) in an aqueous solution.
- Reaction of Li2CO 3with SO 2: Lithium carbonate (Li 2CO 3) reacts with sulfur dioxide (SO 2) in an aqueous solution to form Li 2SO 3.
Chemical Reactions
Li 2SO 3exhibits reactivity in various chemical reactions:
- Reaction with Acids:Li 2SO 3reacts with acids, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), to form lithium chloride (LiCl) and sulfurous acid (H 2SO 3).
- Oxidation:Li 2SO 3can be oxidized to form lithium sulfate (Li 2SO 4) in the presence of an oxidizing agent, such as potassium permanganate (KMnO 4).
- Thermal Decomposition:When heated to high temperatures, Li 2SO 3decomposes to form lithium oxide (Li 2O) and sulfur dioxide (SO 2).
Reactivity and Stability
Li 2SO 3is generally stable under ambient conditions. However, it is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from the air, and can form hydrates.
The chemical compound bf3 li2so3 b2 so3 3 lif is a fascinating subject to explore. If you’re looking to delve deeper into scientific concepts, I highly recommend checking out the apes unit 2 study guide . It’s a great resource for understanding the intricacies of the natural world.
Returning to bf3 li2so3 b2 so3 3 lif, this compound exhibits unique properties that continue to intrigue researchers.
Reaction Table
| Reaction | Reagents | Products |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction with Acids | Li2SO3 + 2HCl → 2LiCl + H2SO3 | Lithium chloride, sulfurous acid |
| Oxidation | Li2SO3 + 2KMnO4 + H2SO4 → Li2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + K2SO4 + H2O | Lithium sulfate, manganese sulfate, potassium sulfate, water |
| Thermal Decomposition | Li2SO3 → Li2O + SO2 | Lithium oxide, sulfur dioxide |
Applications and Uses: Bf3 Li2so3 B2 So3 3 Lif

BF 3•Li 2SO 3•B 2SO 3•3LiF is a versatile compound with numerous applications in various fields.
Industry
- As a catalyst in the production of fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and polymers.
- As a flux in the welding and soldering of metals.
- As a component in the manufacture of glass and ceramics.
Medicine
- As a contrast agent in medical imaging, particularly in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- As a potential treatment for certain types of cancer, due to its ability to inhibit cell growth.
Research
- As a model system for studying the behavior of ionic liquids and their interactions with other molecules.
- As a precursor for the synthesis of novel materials with unique properties.
Common Queries
What is the molecular weight of BF3·Li2SO3·B2O3·3LiF?
The molecular weight of BF3·Li2SO3·B2O3·3LiF is 293.88 g/mol.
What is the solubility of BF3·Li2SO3·B2O3·3LiF in water?
BF3·Li2SO3·B2O3·3LiF is soluble in water.
What are some applications of BF3·Li2SO3·B2O3·3LiF?
BF3·Li2SO3·B2O3·3LiF is used as a flux in soldering and brazing, as a catalyst in organic synthesis, and as a component in optical glasses.